关系
关系是 Prisma 模式中两个模型之间的连接。例如,User 和 Post 之间存在一对多关系,因为一个用户可以拥有多篇博客文章。
¥A relation is a connection between two models in the Prisma schema. For example, there is a one-to-many relation between User and Post because one user can have many blog posts.
以下 Prisma 架构定义了 User 和 Post 模型之间的一对多关系。高亮涉及定义关系的字段:
¥The following Prisma schema defines a one-to-many relation between the User and Post models. The fields involved in defining the relation are highlighted:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
在 Prisma ORM 级别,User / Post 关系由以下部分组成:
¥At a Prisma ORM level, the User / Post relation is made up of:
-
两个 关系字段:
author和posts。关系字段定义 Prisma ORM 级别的模型之间的连接,并且不存在于数据库中。这些字段用于生成 Prisma 客户端。¥Two relation fields:
authorandposts. Relation fields define connections between models at the Prisma ORM level and do not exist in the database. These fields are used to generate Prisma Client. -
标量
authorId字段,由@relation属性引用。该字段在数据库中确实存在 - 它是连接Post和User的外键。¥The scalar
authorIdfield, which is referenced by the@relationattribute. This field does exist in the database - it is the foreign key that connectsPostandUser.
在 Prisma ORM 级别,两个模型之间的连接始终由关系两侧的 关系域 表示。
¥At a Prisma ORM level, a connection between two models is always represented by a relation field on each side of the relation.
数据库中的关系
¥Relations in the database
关系数据库
¥Relational databases
下面的实体关系图定义了关系数据库中 User 和 Post 表之间相同的一对多关系:
¥The following entity relationship diagram defines the same one-to-many relation between the User and Post tables in a relational database:
在 SQL 中,你使用外键在两个表之间创建关系。外键存储在关系的一侧。我们的示例由以下部分组成:
¥In SQL, you use a foreign key to create a relation between two tables. Foreign keys are stored on one side of the relation. Our example is made up of:
-
Post表中名为authorId的外键列。¥A foreign key column in the
Posttable namedauthorId. -
User表中名为id的主键列。Post表中的authorId列引用User表中的id列。¥A primary key column in the
Usertable namedid. TheauthorIdcolumn in thePosttable references theidcolumn in theUsertable.
在 Prisma 模式中,外键/主键关系由 author 字段上的 @relation 属性表示:
¥In the Prisma schema, the foreign key / primary key relationship is represented by the @relation attribute on the author field:
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
注意:Prisma 模式中的关系表示数据库中表之间存在的关系。如果数据库中不存在该关系,则 Prisma 模式中也不存在该关系。
¥Note: Relations in the Prisma schema represent relationships that exist between tables in the database. If the relationship does not exist in the database, it does not exist in the Prisma schema.
MongoDB
对于 MongoDB,Prisma ORM 目前使用 规范化数据模型设计,这意味着文档以与关系数据库类似的方式通过 ID 相互引用。
¥For MongoDB, Prisma ORM currently uses a normalized data model design, which means that documents reference each other by ID in a similar way to relational databases.
以下文档代表 User(在 User 集合中):
¥The following document represents a User (in the User collection):
{ "_id": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }, "name": "Ella" }
以下 Post 文档列表(在 Post 集合中)每个文档都有一个引用同一用户的 authorId 字段:
¥The following list of Post documents (in the Post collection) each have a authorId field which reference the same user:
[
{
"_id": { "$oid": "60d5922e00581b8f0062e3a9" },
"title": "How to make sushi",
"authorId": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }
},
{
"_id": { "$oid": "60d5922e00581b8f0062e3aa" },
"title": "How to re-install Windows",
"authorId": { "$oid": "60d5922d00581b8f0062e3a8" }
}
]
该数据结构表示一对多关系,因为多个 Post 文档引用同一个 User 文档。
¥This data structure represents a one-to-many relation because multiple Post documents refer to the same User document.
ID 和关系标量字段上的 @db.ObjectId
¥@db.ObjectId on IDs and relation scalar fields
如果模型的 ID 是 ObjectId(由 String 字段表示),则必须将 @db.ObjectId 添加到模型的 ID 和关系另一侧的关系标量字段:
¥If your model's ID is an ObjectId (represented by a String field), you must add @db.ObjectId to the model's ID and the relation scalar field on the other side of the relation:
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
title String
}
Prisma 客户端中的关系
¥Relations in Prisma Client
Prisma 客户端是从 Prisma 架构生成的。以下示例演示了当你使用 Prisma 客户端获取、创建和更新记录时关系如何体现。
¥Prisma Client is generated from the Prisma schema. The following examples demonstrate how relations manifest when you use Prisma Client to get, create, and update records.
创建记录和嵌套记录
¥Create a record and nested records
以下查询创建一条 User 记录和两条连接的 Post 记录:
¥The following query creates a User record and two connected Post records:
const userAndPosts = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
posts: {
create: [
{ title: 'Prisma Day 2020' }, // Populates authorId with user's id
{ title: 'How to write a Prisma schema' }, // Populates authorId with user's id
],
},
},
})
在底层数据库中,此查询:
¥In the underlying database, this query:
-
使用自动生成的
id创建User(例如20)¥Creates a
Userwith an auto-generatedid(for example,20) -
创建两条新的
Post记录并将两条记录的authorId设置为20¥Creates two new
Postrecords and sets theauthorIdof both records to20
检索记录并包含相关记录
¥Retrieve a record and include related records
以下查询通过 id 检索 User 并包括任何相关的 Post 记录:
¥The following query retrieves a User by id and includes any related Post records:
const getAuthor = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {
id: "20",
},
include: {
posts: true, // All posts where authorId == 20
},
});
在底层数据库中,此查询:
¥In the underlying database, this query:
-
检索
User记录,其中id为20¥Retrieves the
Userrecord with anidof20 -
检索
authorId为20的所有Post记录¥Retrieves all
Postrecords with anauthorIdof20
将现有记录关联到另一个现有记录
¥Associate an existing record to another existing record
以下查询将现有 Post 记录与现有 User 记录关联:
¥The following query associates an existing Post record with an existing User record:
const updateAuthor = await prisma.user.update({
where: {
id: 20,
},
data: {
posts: {
connect: {
id: 4,
},
},
},
})
在底层数据库中,此查询使用 嵌套 connect 查询 将 id 为 4 的帖子链接到 id 为 20 的用户。该查询通过以下步骤执行此操作:
¥In the underlying database, this query uses a nested connect query to link the post with an id of 4 to the user with an id of 20. The query does this with the following steps:
-
该查询首先查找
id为20的用户。¥The query first looks for the user with an
idof20. -
然后查询将
authorID外键设置为20。这会将id或4的帖子链接到id或20的用户。¥The query then sets the
authorIDforeign key to20. This links the post with anidof4to the user with anidof20.
在此查询中,authorID 的当前值并不重要。查询将 authorID 更改为 20,无论其当前值如何。
¥In this query, the current value of authorID does not matter. The query changes authorID to 20, no matter its current value.
关系类型
¥Types of relations
Prisma ORM 中有三种不同类型(或 cardinalities)的关系:
¥There are three different types (or cardinalities) of relations in Prisma ORM:
-
一对一(也称为 1-1 关系)
¥One-to-one (also called 1-1 relations)
-
一对多(也称为 1-n 关系)
¥One-to-many (also called 1-n relations)
-
多对多(也称为 m-n 关系)
¥Many-to-many (also called m-n relations)
以下 Prisma 架构包括每种类型的关系:
¥The following Prisma schema includes every type of relation:
-
一对一:
User↔Profile¥one-to-one:
User↔Profile -
一对多:
User↔Post¥one-to-many:
User↔Post -
多对多:
Post↔Category¥many-to-many:
Post↔Category
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int @unique // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
categories Category[]
}
model Category {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
posts Post[]
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId String @unique @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
categories Category[] @relation(fields: [categoryIds], references: [id])
categoryIds String[] @db.ObjectId
}
model Category {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
posts Post[] @relation(fields: [postIds], references: [id])
postIds String[] @db.ObjectId
}
此架构与 示例数据模型 相同,但删除了所有 标量场(所需的 关系标量场 除外),因此你可以专注于 关系字段。
¥This schema is the same as the example data model but has all scalar fields removed (except for the required relation scalar fields) so you can focus on the relation fields.
本例使用 隐式多对多关系。这些关系不需要 @relation 属性,除非你需要 消除关系的歧义。
¥This example uses implicit many-to-many relations. These relations do not require the @relation attribute unless you need to disambiguate relations.
请注意,关系数据库和 MongoDB 之间的语法略有不同 - 特别是对于 多对多关系。
¥Notice that the syntax is slightly different between relational databases and MongoDB - particularly for many-to-many relations.
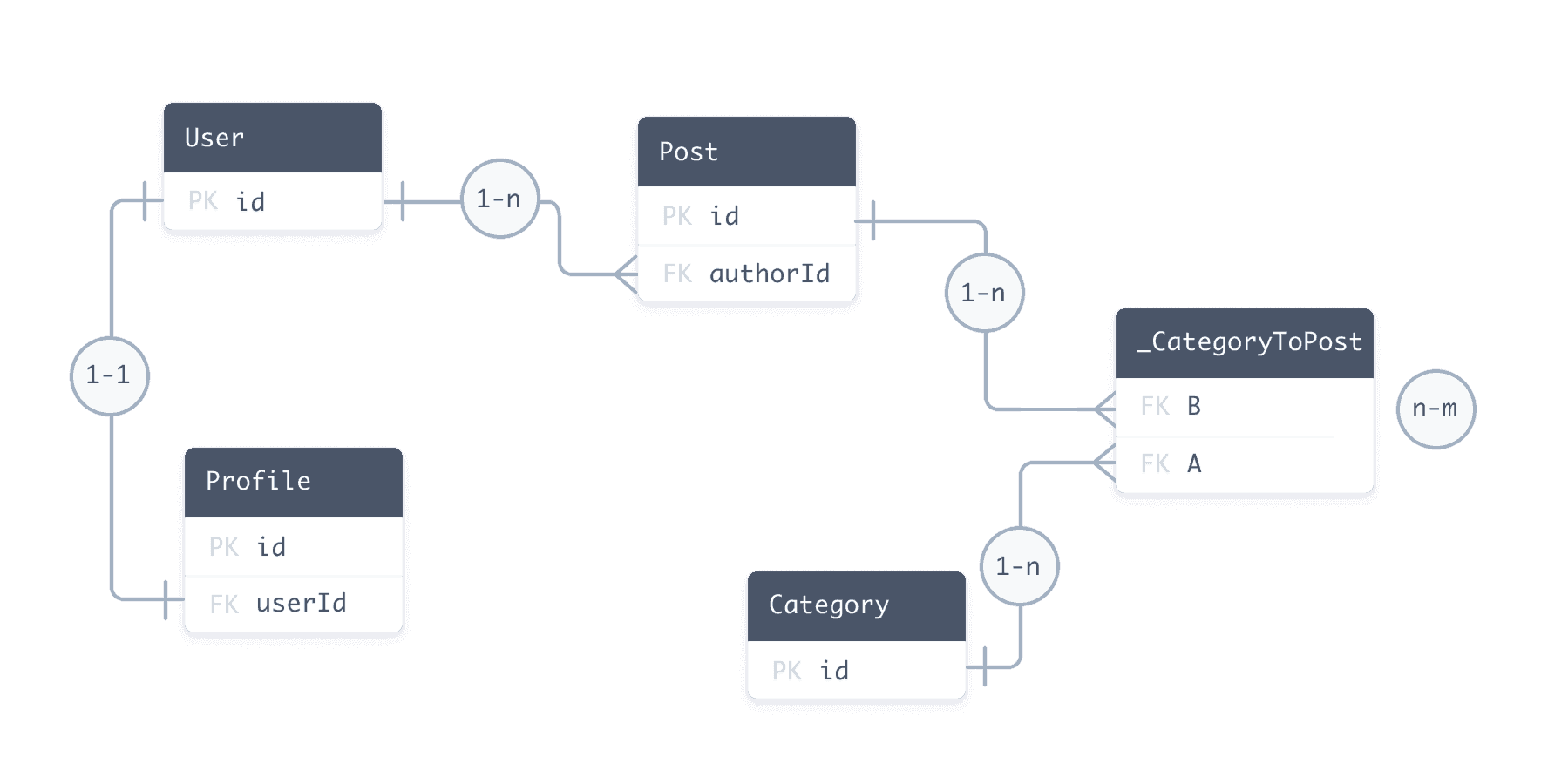
对于关系数据库,以下实体关系图表示与示例 Prisma 架构对应的数据库:
¥For relational databases, the following entity relationship diagram represents the database that corresponds to the sample Prisma schema:
对于 MongoDB,Prisma ORM 使用 规范化数据模型设计,这意味着文档通过 ID 相互引用,方式与关系数据库类似。详细信息请参见 MongoDB 部分。
¥For MongoDB, Prisma ORM uses a normalized data model design, which means that documents reference each other by ID in a similar way to relational databases. See the MongoDB section for more details.
隐式和显式多对多关系
¥Implicit and explicit many-to-many relations
关系数据库中的多对多关系可以通过两种方式建模:
¥Many-to-many relations in relational databases can be modelled in two ways:
-
显式多对多关系,其中关系表在 Prisma 模式中表示为显式模型
¥explicit many-to-many relations, where the relation table is represented as an explicit model in your Prisma schema
-
隐式多对多关系,其中 Prisma ORM 管理关系表,它不会出现在 Prisma 模式中。
¥implicit many-to-many relations, where Prisma ORM manages the relation table and it does not appear in the Prisma schema.
隐式多对多关系要求两个模型都具有单个 @id。请注意以下事项:
¥Implicit many-to-many relations require both models to have a single @id. Be aware of the following:
-
你不能使用 多字段 ID
¥You cannot use a multi-field ID
-
你不能使用
@unique代替@id¥You cannot use a
@uniquein place of an@id
要使用这些功能中的任何一个,你必须设置显式的多对多。
¥To use either of these features, you must set up an explicit many-to-many instead.
隐式多对多关系仍然体现在底层数据库的关系表中。然而,Prisma ORM 管理这个关系表。
¥The implicit many-to-many relation still manifests in a relation table in the underlying database. However, Prisma ORM manages this relation table.
如果你使用隐式多对多关系而不是显式关系,则会使 Prisma 客户端 API 更简单(因为,例如,你在 嵌套写入 内部的嵌套级别会少一层)。
¥If you use an implicit many-to-many relation instead of an explicit one, it makes the Prisma Client API simpler (because, for example, you have one fewer level of nesting inside of nested writes).
如果你不使用 Prisma Migrate,而是从 introspection 获取数据模型,你仍然可以按照 Prisma ORM 的 关系表的约定 使用隐式多对多关系。
¥If you're not using Prisma Migrate but obtain your data model from introspection, you can still make use of implicit many-to-many relations by following Prisma ORM's conventions for relation tables.
关系字段
¥Relation fields
关系 fields 是 Prisma model 上没有 标量类型 的字段。相反,他们的类型是另一种模式。
¥Relation fields are fields on a Prisma model that do not have a scalar type. Instead, their type is another model.
每个关系必须恰好有两个关系字段,每个模型都有一个。在一对一和一对多关系的情况下,需要一个附加的关系标量字段,该字段由 @relation 属性中的两个关系字段之一链接。此关系标量字段是底层数据库中外键的直接表示。
¥Every relation must have exactly two relation fields, one on each model. In the case of one-to-one and one-to-many relations, an additional relation scalar field is required which gets linked by one of the two relation fields in the @relation attribute. This relation scalar field is the direct representation of the foreign key in the underlying database.
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[] // relation field (defined only at the Prisma ORM level)
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id]) // relation field (uses the relation scalar field `authorId` below)
authorId Int // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[] // relation field (defined only at the Prisma ORM level)
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id]) // relation field (uses the relation scalar field `authorId` below)
authorId String @db.ObjectId // relation scalar field (used in the `@relation` attribute above)
}
posts 和 author 都是关系字段,因为它们的类型不是标量类型而是其他模型。
¥Both posts and author are relation fields because their types are not scalar types but other models.
另请注意,带注释的关系字段 author 需要将关系标量字段 authorId 链接到 @relation 属性内的 Post 模型上。关系标量字段表示底层数据库中的外键。
¥Also note that the annotated relation field author needs to link the relation scalar field authorId on the Post model inside the @relation attribute. The relation scalar field represents the foreign key in the underlying database.
两个关系字段(即 posts 和 author)都是在 Prisma ORM 级别定义的,它们不会在数据库中体现。
¥Both the relation fields (i.e. posts and author) are defined purely on a Prisma ORM-level, they don't manifest in the database.
带注释的关系字段
¥Annotated relation fields
需要用 @relation 属性注释关系一侧的关系称为注释关系字段。这包括:
¥Relations that require one side of the relation to be annotated with the @relation attribute are referred to as annotated relation fields. This includes:
-
一对一的关系
¥one-to-one relations
-
一对多关系
¥one-to-many relations
-
仅适用于 MongoDB 的多对多关系
¥many-to-many relations for MongoDB only
关系中用 @relation 属性注释的一侧表示在底层数据库中存储外键的一侧。表示外键的 "actual" 字段在关系的这一侧也是必需的,它称为关系标量字段,并在 @relation 属性内引用:
¥The side of the relation which is annotated with the @relation attribute represents the side that stores the foreign key in the underlying database. The "actual" field that represents the foreign key is required on that side of the relation as well, it's called relation scalar field, and is referenced inside @relation attribute:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
当标量字段用在 @relation 属性的 fields 中时,它就成为关系标量字段。
¥A scalar field becomes a relation scalar field when it's used in the fields of a @relation attribute.
关系标量场
¥Relation scalar fields
关系标量字段命名约定
¥Relation scalar field naming conventions
由于关系标量字段始终属于关系字段,因此以下命名约定是常见的:
¥Because a relation scalar field always belongs to a relation field, the following naming convention is common:
-
关系字段:
author¥Relation field:
author -
关系标量场:
authorId(关系字段名+Id)¥Relation scalar field:
authorId(relation field name +Id)
@relation 属性
¥The @relation attribute
@relation 属性只能应用于 关系字段,不能应用于 标量场。
¥The @relation attribute can only be applied to the relation fields, not to scalar fields.
在以下情况下需要 @relation 属性:
¥The @relation attribute is required when:
-
你定义一对一或一对多关系,该关系的一侧需要它(具有相应的关系标量字段)
¥you define a one-to-one or one-to-many relation, it is required on one side of the relation (with the corresponding relation scalar field)
-
你需要消除关系的歧义(例如,当同一模型之间有两个关系时就是这种情况)
¥you need to disambiguate a relation (that's e.g. the case when you have two relations between the same models)
-
你定义了一个 自我关系
¥you define a self-relation
-
你定义 MongoDB 的多对多关系
¥you define a many-to-many relation for MongoDB
-
你需要控制关系表在基础数据库中的表示方式(例如,为关系表使用特定名称)
¥you need to control how the relation table is represented in the underlying database (e.g. use a specific name for a relation table)
注意:关系数据库中的 隐式多对多关系 不需要
@relation属性。¥Note: Implicit many-to-many relations in relational databases do not require the
@relationattribute.
消除关系歧义
¥Disambiguating relations
当你在相同的两个模型之间定义两个关系时,你需要在 @relation 属性中添加 name 参数以消除它们的歧义。作为为什么需要这样做的示例,请考虑以下模型:
¥When you define two relations between the same two models, you need to add the name argument in the @relation attribute to disambiguate them. As an example for why that's needed, consider the following models:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
// NOTE: This schema is intentionally incorrect. See below for a working solution.
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String?
writtenPosts Post[]
pinnedPost Post?
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String?
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
pinnedBy User? @relation(fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById Int?
}
// NOTE: This schema is intentionally incorrect. See below for a working solution.
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String?
writtenPosts Post[]
pinnedPost Post?
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String?
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
pinnedBy User? @relation(fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById String? @db.ObjectId
}
在这种情况下,关系是不明确的,有四种不同的方式来解释它们:
¥In that case, the relations are ambiguous, there are four different ways to interpret them:
-
User.writtenPosts↔Post.author+Post.authorId -
User.writtenPosts↔Post.pinnedBy+Post.pinnedById -
User.pinnedPost↔Post.author+Post.authorId -
User.pinnedPost↔Post.pinnedBy+Post.pinnedById
要消除这些关系的歧义,你需要使用 @relation 属性注释关系字段并提供 name 参数。你可以设置任何 name(空字符串 "" 除外),但关系两侧必须相同:
¥To disambiguate these relations, you need to annotate the relation fields with the @relation attribute and provide the name argument. You can set any name (except for the empty string ""), but it must be the same on both sides of the relation:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String?
writtenPosts Post[] @relation("WrittenPosts")
pinnedPost Post? @relation("PinnedPost")
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String?
author User @relation("WrittenPosts", fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
pinnedBy User? @relation("PinnedPost", fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById Int? @unique
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String?
writtenPosts Post[] @relation("WrittenPosts")
pinnedPost Post? @relation("PinnedPost")
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String?
author User @relation("WrittenPosts", fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
pinnedBy User? @relation("PinnedPost", fields: [pinnedById], references: [id])
pinnedById String? @unique @db.ObjectId
}