模块
Prisma 架构 的数据模型定义部分定义了你的应用模型(也称为 Prisma 模型)。模块:
¥The data model definition part of the Prisma schema defines your application models (also called Prisma models). Models:
-
代表你的应用域的实体
¥Represent the entities of your application domain
-
映射到数据库中的表(关系数据库,如 PostgreSQL)或集合 (MongoDB)
¥Map to the tables (relational databases like PostgreSQL) or collections (MongoDB) in your database
-
形成生成的 Prisma 客户端 API 中可用查询的基础
¥Form the foundation of the queries available in the generated Prisma Client API
-
当与 TypeScript 一起使用时,Prisma Client 为你的模型及其任何 variations 提供生成的类型定义,以使数据库访问完全类型安全。
¥When used with TypeScript, Prisma Client provides generated type definitions for your models and any variations of them to make database access entirely type safe.
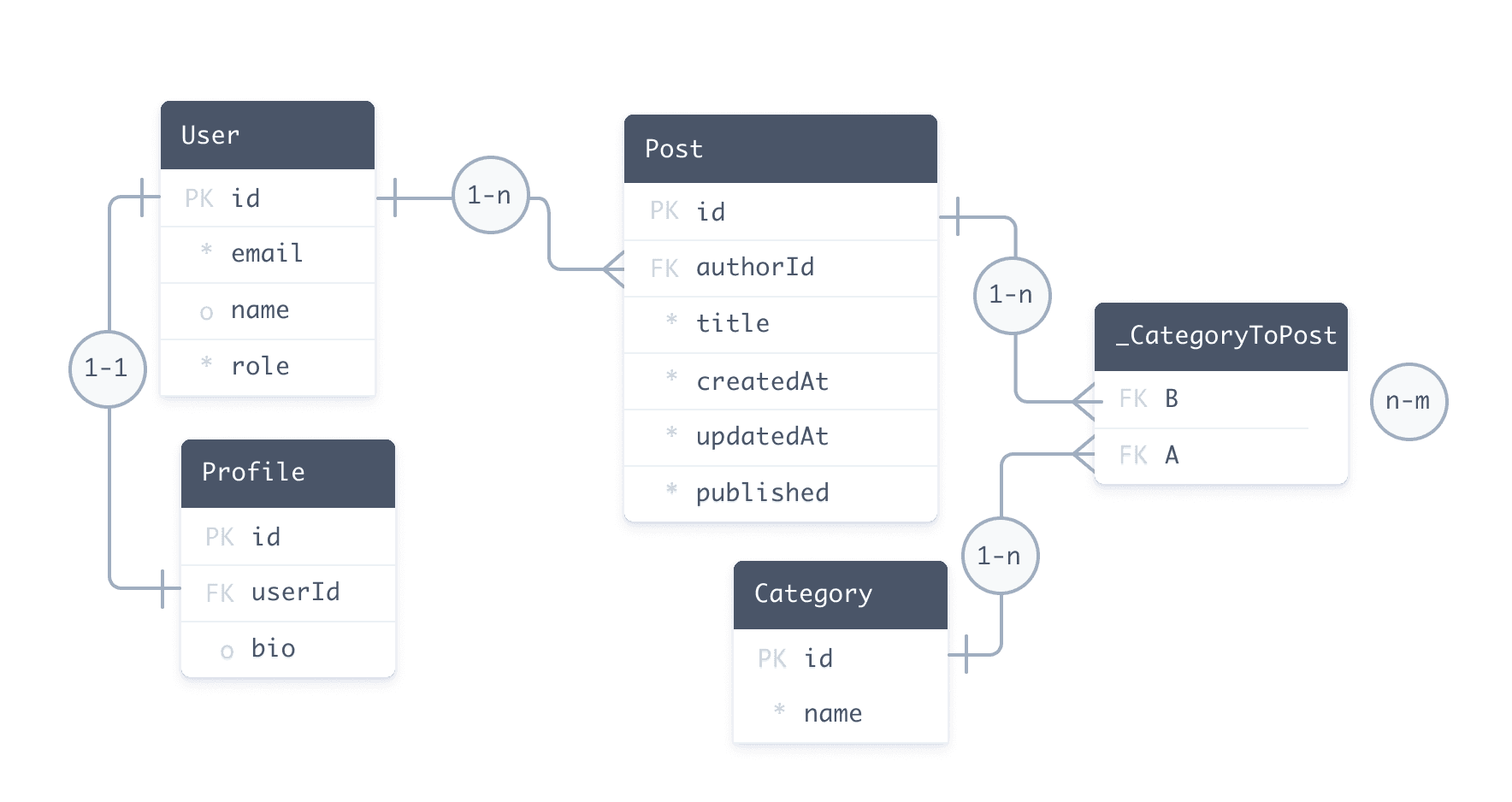
以下架构描述了一个博客平台 - 数据模型定义高亮:
¥The following schema describes a blogging platform - the data model definition is highlighted:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client"
output = "./generated"
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
bio String
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int @unique
}
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @updatedAt
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
categories Category[]
}
model Category {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String
posts Post[]
}
enum Role {
USER
ADMIN
}
datasource db {
provider = "mongodb"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
model Profile {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
bio String
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId String @unique @db.ObjectId
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
categoryIDs String[] @db.ObjectId
categories Category[] @relation(fields: [categoryIDs], references: [id])
}
model Category {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String
postIDs String[] @db.ObjectId
posts Post[] @relation(fields: [postIDs], references: [id])
}
enum Role {
USER
ADMIN
}
数据模型定义由以下部分组成:
¥The data model definition is made up of:
-
模块(
model原语)定义了许多字段,包括 模型之间的关系¥Models (
modelprimitives) that define a number of fields, including relations between models -
¥Attributes and functions that change the behavior of fields and models
对应的数据库如下所示:
¥The corresponding database looks like this:
A model maps to the underlying structures of the data source.
-
在 PostgreSQL 和 MySQL 等关系数据库中,
model映射到表¥In relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL, a
modelmaps to a table -
在 MongoDB 中,
model映射到集合¥In MongoDB, a
modelmaps to a collection
注意:将来可能会有用于非关系数据库和其他数据源的连接器。例如,对于 REST API,它将映射到资源。
¥Note: In the future there might be connectors for non-relational databases and other data sources. For example, for a REST API it would map to a resource.
以下查询使用从此数据模型生成的 Prisma Client 来创建:
¥The following query uses Prisma Client that's generated from this data model to create:
-
User记录¥A
Userrecord -
两个嵌套的
Post记录¥Two nested
Postrecords -
三个嵌套
Category记录¥Three nested
Categoryrecords
- Query Example
- Copy-Paste Example
const user = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
email: 'ariadne@prisma.io',
name: 'Ariadne',
posts: {
create: [
{
title: 'My first day at Prisma',
categories: {
create: {
name: 'Office',
},
},
},
{
title: 'How to connect to a SQLite database',
categories: {
create: [{ name: 'Databases' }, { name: 'Tutorials' }],
},
},
],
},
},
})
import { PrismaClient } from '../prisma/generated/client'
const prisma = new PrismaClient({})
// A `main` function so that you can use async/await
async function main() {
// Create user, posts, and categories
const user = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
email: 'ariadne@prisma.io',
name: 'Ariadne',
posts: {
create: [
{
title: 'My first day at Prisma',
categories: {
create: {
name: 'Office',
},
},
},
{
title: 'How to connect to a SQLite database',
categories: {
create: [{ name: 'Databases' }, { name: 'Tutorials' }],
},
},
],
},
},
})
// Return user, and posts, and categories
const returnUser = await prisma.user.findUnique({
where: {
id: user.id,
},
include: {
posts: {
include: {
categories: true,
},
},
},
})
console.log(returnUser)
}
main()
你的数据模型反映了你的应用域。例如:
¥Your data model reflects your application domain. For example:
-
在电子商务应用中,你可能有
Customer、Order、Item和Invoice等模型。¥In an ecommerce application you probably have models like
Customer,Order,ItemandInvoice. -
在社交媒体应用中,你可能有
User、Post、Photo和Message等模型。¥In a social media application you probably have models like
User,Post,PhotoandMessage.
自省与迁移
¥Introspection and migration
定义数据模型有两种方法:
¥There are two ways to define a data model:
-
手动编写数据模型并使用 Prisma Migrate:你可以手动编写数据模型并使用 Prisma 迁移 将其映射到数据库。在这种情况下,数据模型是应用模型的单一事实来源。
¥Write the data model manually and use Prisma Migrate: You can write your data model manually and map it to your database using Prisma Migrate. In this case, the data model is the single source of truth for the models of your application.
-
通过内省生成数据模型:当你拥有现有数据库或更喜欢使用 SQL 迁移数据库架构时,你可以通过 introspecting 数据库生成数据模型。在这种情况下,数据库模式是应用模型的唯一事实来源。
¥Generate the data model via introspection: When you have an existing database or prefer migrating your database schema with SQL, you generate the data model by introspecting your database. In this case, the database schema is the single source of truth for the models of your application.
定义模型
¥Defining models
模型代表应用域的实体。模型由 model 块表示并定义了多个 fields。在上面的示例数据模型中,User、Profile、Post 和 Category 是模型。
¥Models represent the entities of your application domain. Models are represented by model blocks and define a number of fields. In the example data model above, User, Profile, Post and Category are models.
博客平台可以通过以下模型进行扩展:
¥A blogging platform can be extended with the following models:
model Comment {
// Fields
}
model Tag {
// Fields
}
将模型名称映射到表或集合
¥Mapping model names to tables or collections
Prisma 型号 命名约定(单数形式、PascalCase) 并不总是与数据库中的表名称匹配。在数据库中命名表/集合的常见方法是使用复数形式和 蛇箱 表示法 - 例如:comments。当你内省包含名为 comments 的表的数据库时,结果 Prisma 模型将如下所示:
¥Prisma model naming conventions (singular form, PascalCase) do not always match table names in the database. A common approach for naming tables/collections in databases is to use plural form and snake_case notation - for example: comments. When you introspect a database with a table named comments, the result Prisma model will look like this:
model comments {
// Fields
}
但是,你仍然可以遵守命名约定,而无需使用 @@map 属性重命名数据库中的基础 comments 表:
¥However, you can still adhere to the naming convention without renaming the underlying comments table in the database by using the @@map attribute:
model Comment {
// Fields
@@map("comments")
}
通过此模型定义,Prisma ORM 自动将 Comment 模型映射到底层数据库中的 comments 表。
¥With this model definition, Prisma ORM automatically maps the Comment model to the comments table in the underlying database.
注意:你还可以
@map列名称或枚举值,并@@map枚举名称。¥Note: You can also
@mapa column name or enum value, and@@mapan enum name.
@map 和 @@map 允许你通过将模型和字段名称与基础数据库中的表和列名称解耦来实现 调整 Prisma 客户端 API 的形状。
¥@map and @@map allow you to tune the shape of your Prisma Client API by decoupling model and field names from table and column names in the underlying database.
定义字段
¥Defining fields
模型的属性称为字段,其中包括:
¥The properties of a model are called fields, which consist of:
-
一个 字段名称
¥A field name
-
一个 字段类型
¥A field type
-
可选 类型修饰符
¥Optional type modifiers
-
可选 attributes,包括 原生数据库类型属性
¥Optional attributes, including native database type attributes
字段的类型决定其结构,并且适合以下两个类别之一:
¥A field's type determines its structure, and fits into one of two categories:
-
映射到数据库中的列(关系数据库)或文档字段(MongoDB)的 标量类型(包括 enums) - 例如,
String或Int¥Scalar types (includes enums) that map to columns (relational databases) or document fields (MongoDB) in the database - for example,
StringorInt -
模型类型(该字段随后称为 关系域) - 例如
Post或Comment[]。¥Model types (the field is then called relation field) - for example
PostorComment[].
下表描述了示例架构中 User 模型的字段:
¥The following table describes User model's fields from the sample schema:
Expand to see table
| 名称 | 类型 | 标量与关系 | 类型修饰符 | 属性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
id | Int | 标量 | * | @id 和 @default(autoincrement()) |
email | String | 标量 | * | @unique |
name | String | 标量 | ? | * |
role | Role | 标量 (enum) | * | @default(USER) |
posts | Post | 关系(Prisma 级场) | [] | * |
profile | Profile | 关系(Prisma 级场) | ? | * |
标量场
¥Scalar fields
以下示例使用多种标量类型扩展了 Comment 和 Tag 模型。一些字段包括 attributes:
¥The following example extends the Comment and Tag models with several scalar types. Some fields include attributes:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Comment {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
content String
}
model Tag {
name String @id
}
model Comment {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String
content String
}
model Tag {
name String @id @map("_id")
}
参见 标量字段类型的完整列表。
¥See complete list of scalar field types .
关系字段
¥Relation fields
关系字段的类型是另一种模型 - 例如,一个帖子 (Post) 可以有多个评论 (Comment[]):
¥A relation field's type is another model - for example, a post (Post) can have multiple comments (Comment[]):
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
// Other fields
comments Comment[] // A post can have many comments
}
model Comment {
id Int
// Other fields
post Post? @relation(fields: [postId], references: [id]) // A comment can have one post
postId Int?
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.Objectid
// Other fields
comments Comment[] // A post can have many comments
}
model Comment {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.Objectid
// Other fields
post Post? @relation(fields: [postId], references: [id]) // A comment can have one post
postId String? @db.ObjectId
}
有关模型之间关系的更多示例和信息,请参阅 关系文档。
¥Refer to the relations documentation for more examples and information about relationships between models.
原生类型映射
¥Native types mapping
版本 2.17.0 及更高版本支持描述底层数据库类型的原生数据库类型属性(type attribute):
¥Version 2.17.0 and later support native database type attributes (type attributes) that describe the underlying database type:
model Post {
id Int @id
title String @db.VarChar(200)
content String
}
类型属性有:
¥Type attributes are:
-
特定于底层提供商 - 例如,PostgreSQL 使用
@db.Boolean代表Boolean,而 MySQL 使用@db.TinyInt(1)¥Specific to the underlying provider - for example, PostgreSQL uses
@db.BooleanforBooleanwhereas MySQL uses@db.TinyInt(1) -
以 PascalCase 编写(例如
VarChar或Text)¥Written in PascalCase (for example,
VarCharorText) -
以
@db为前缀,其中db是架构中datasource块的名称¥Prefixed by
@db, wheredbis the name of thedatasourceblock in your schema
此外,在 内省 期间,仅当底层原生类型不是默认类型时,类型属性才会添加到架构中。例如,如果你使用 PostgreSQL 提供程序,则基础原生类型为 text 的 String 字段将没有类型属性。
¥Furthermore, during Introspection type attributes are only added to the schema if the underlying native type is not the default type. For example, if you are using the PostgreSQL provider, String fields where the underlying native type is text will not have a type attribute.
参见 每个标量类型和提供程序的原生数据库类型属性的完整列表。
¥See complete list of native database type attributes per scalar type and provider .
优点和工作流程
¥Benefits and workflows
-
控制 Prisma 迁移 在数据库中创建的确切原生类型 - 例如,
String可以是@db.VarChar(200)或@db.Char(50)¥Control the exact native type that Prisma Migrate creates in the database - for example, a
Stringcan be@db.VarChar(200)or@db.Char(50) -
内省时看到丰富的模式
¥See an enriched schema when you introspect
类型修饰符
¥Type modifiers
可以通过附加两个修饰符之一来修改字段的类型:
¥The type of a field can be modified by appending either of two modifiers:
注意:不能组合类型修饰符 - 不支持可选列表。
¥Note: You cannot combine type modifiers - optional lists are not supported.
列表
¥Lists
以下示例包括标量列表和相关模型的列表:
¥The following example includes a scalar list and a list of related models:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
// Other fields
comments Comment[] // A list of comments
keywords String[] // A scalar list
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
// Other fields
comments Comment[] // A list of comments
keywords String[] // A scalar list
}
注意:仅当数据库连接器本身支持标量列表或在 Prisma ORM 级别支持标量列表时,才支持标量列表。
¥Note: Scalar lists are only supported if the database connector supports scalar lists, either natively or at a Prisma ORM level.
可选和必填字段
¥Optional and mandatory fields
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Comment {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
content String?
}
model Tag {
name String @id
}
model Comment {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
title String
content String?
}
model Tag {
name String @id @map("_id")
}
当不使用 ? 类型修饰符注释字段时,模型的每个记录都需要该字段。这在两个层面上产生影响:
¥When not annotating a field with the ? type modifier, the field will be required on every record of the model. This has effects on two levels:
-
数据库
¥Databases
-
关系数据库:必填字段通过底层数据库中的
NOT NULL约束表示。¥Relational databases: Required fields are represented via
NOT NULLconstraints in the underlying database. -
MongoDB:必填字段不是 MongoDB 数据库级别的概念。
¥MongoDB: Required fields are not a concept on a MongoDB database level.
-
-
Prisma 客户端:Prisma 客户端生成的代表应用代码中模型的 TypeScript 类型 也将根据需要定义这些字段,以确保它们在运行时始终携带值。
¥Prisma Client: Prisma Client's generated TypeScript types that represent the models in your application code will also define these fields as required to ensure they always carry values at runtime.
注意:可选字段的默认值为
null。¥Note: The default value of an optional field is
null.
不支持的类型
¥Unsupported types
当你内省关系数据库时,不支持的数据类型将添加为 Unsupported :
¥When you introspect a relational database, unsupported data types are added as Unsupported :
location Unsupported("POLYGON")?
Unsupported 类型允许你在 Prisma 架构中为 Prisma ORM 尚不支持的数据库类型定义字段。例如,Prisma ORM 目前不支持 MySQL 的 POLYGON 类型,但现在可以使用 Unsupported("POLYGON") 类型将其添加到 Prisma 架构中。
¥The Unsupported type allows you to define fields in the Prisma schema for database types that are not yet supported by Prisma ORM. For example, MySQL's POLYGON type is not currently supported by Prisma ORM, but can now be added to the Prisma schema using the Unsupported("POLYGON") type.
类型 Unsupported 的字段不会出现在生成的 Prisma 客户端 API 中,但你仍然可以使用 Prisma ORM 的 原始数据库访问功能 来查询这些字段。
¥Fields of type Unsupported do not appear in the generated Prisma Client API, but you can still use Prisma ORM’s raw database access feature to query these fields.
注意:如果模型具有强制
Unsupported字段,则生成的客户端将不会包含该模型的create或update方法。¥Note: If a model has mandatory
Unsupportedfields, the generated client will not includecreateorupdatemethods for that model.
注意:MongoDB 连接器不支持也不需要
Unsupported类型,因为它支持所有标量类型。¥Note: The MongoDB connector does not support nor require the
Unsupportedtype because it supports all scalar types.
定义属性
¥Defining attributes
属性修改字段或模型块的行为。以下示例包括三个字段属性(@id、@default 和 @unique)和一个块属性(@@unique):
¥Attributes modify the behavior of fields or model blocks. The following example includes three field attributes (@id , @default , and @unique ) and one block attribute (@@unique):
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
firstName String
lastName String
email String @unique
isAdmin Boolean @default(false)
@@unique([firstName, lastName])
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
firstName String
lastName String
email String @unique
isAdmin Boolean @default(false)
@@unique([firstName, lastName])
}
某些属性接受 arguments - 例如,@default 接受 true 或 false:
¥Some attributes accept arguments - for example, @default accepts true or false:
isAdmin Boolean @default(false) // short form of @default(value: false)
¥See complete list of field and block attributes
定义 ID 字段
¥Defining an ID field
ID 唯一标识模型的各个记录。一个模型只能有一个 ID:
¥An ID uniquely identifies individual records of a model. A model can only have one ID:
-
在关系数据库中,ID 可以是单个字段,也可以基于多个字段。如果模型没有
@id或@@id,则必须定义强制@unique字段或@@unique块。¥In relational databases, the ID can be a single field or based on multiple fields. If a model does not have an
@idor an@@id, you must define a mandatory@uniquefield or@@uniqueblock instead. -
在 MongoDB 中,ID 必须是定义
@id属性和@map("_id")属性的单个字段。¥In MongoDB, an ID must be a single field that defines an
@idattribute and a@map("_id")attribute.
在关系数据库中定义 ID
¥Defining IDs in relational databases
在关系数据库中,ID 可以使用 @id 属性由单个字段定义,也可以使用 @@id 属性由多个字段定义。
¥In relational databases, an ID can be defined by a single field using the @id attribute, or multiple fields using the @@id attribute.
单字段 ID
¥Single field IDs
在以下示例中,User ID 由 id 整数字段表示:
¥In the following example, the User ID is represented by the id integer field:
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
复合 ID
¥Composite IDs
在以下示例中,User ID 由 firstName 和 lastName 字段的组合表示:
¥In the following example, the User ID is represented by a combination of the firstName and lastName fields:
model User {
firstName String
lastName String
email String @unique
isAdmin Boolean @default(false)
@@id([firstName, lastName])
}
默认情况下,Prisma 客户端查询中该字段的名称将为 firstName_lastName。
¥By default, the name of this field in Prisma Client queries will be firstName_lastName.
你还可以使用 @@id 属性的 name 字段为复合 ID 提供你自己的名称:
¥You can also provide your own name for the composite ID using the @@id attribute's name field:
model User {
firstName String
lastName String
email String @unique
isAdmin Boolean @default(false)
@@id(name: "fullName", fields: [firstName, lastName])
}
firstName_lastName 字段现在将命名为 fullName。
¥The firstName_lastName field will now be named fullName instead.
请参阅 使用复合 ID 上的文档,了解如何与 Prisma 客户端中的复合 ID 进行交互。
¥Refer to the documentation on working with composite IDs to learn how to interact with a composite ID in Prisma Client.
@unique 字段作为唯一标识符
¥@unique fields as unique identifiers
在以下示例中,用户由 @unique 字段唯一标识。由于 email 字段充当模型的唯一标识符(这是必需的),因此它必须是强制性的:
¥In the following example, users are uniquely identified by a @unique field. Because the email field functions as a unique identifier for the model (which is required), it must be mandatory:
model User {
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
关系数据库中的约束名称
你可以选择在基础数据库中定义 自定义主键约束名称。
¥Constraint names in relational databases
You can optionally define a custom primary key constraint name in the underlying database.
在 MongoDB 中定义 ID
¥Defining IDs in MongoDB
MongoDB 连接器具有与关系数据库不同的 定义 ID 字段的具体规则。ID 必须由使用 @id 属性的单个字段定义,并且必须包含 @map("_id")。
¥The MongoDB connector has specific rules for defining an ID field that differs from relational databases. An ID must be defined by a single field using the @id attribute and must include @map("_id").
在以下示例中,User ID 由接受自动生成的 ObjectId 的 id 字符串字段表示:
¥In the following example, the User ID is represented by the id string field that accepts an auto-generated ObjectId:
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
在以下示例中,User ID 由 id 字符串字段表示,该字段接受 ObjectId 以外的内容 - 例如,一个唯一的用户名:
¥In the following example, the User ID is represented by the id string field that accepts something other than an ObjectId - for example, a unique username:
model User {
id String @id @map("_id")
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
MongoDB 不支持 @@id
MongoDB 不支持复合 ID,这意味着你无法识别具有 @@id 块的模型。
¥MongoDB does not support @@id
MongoDB does not support composite IDs, which means you cannot identify a model with a @@id block.
定义默认值
¥Defining a default value
你可以使用 @default 属性为模型的标量字段定义默认值:
¥You can define default values for scalar fields of your models using the @default attribute:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
data Json @default("{ \"hello\": \"world\" }")
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
categories Category[] @relation(references: [id])
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
categories Category[] @relation(references: [id])
}
@default 属性:
¥@default attributes either:
-
表示底层数据库中的
DEFAULT值(仅限关系数据库)或¥Represent
DEFAULTvalues in the underlying database (relational databases only) or -
使用 Prisma ORM 级别的函数。例如,
cuid()和uuid()由 Prisma Client 的 查询引擎 为所有连接器提供。¥Use a Prisma ORM-level function. For example,
cuid()anduuid()are provided by Prisma Client's query engine for all connectors.
默认值可以是:
¥Default values can be:
-
与字段类型对应的静态值,例如
5(Int)、Hello(String) 或false(Boolean)¥Static values that correspond to the field type, such as
5(Int),Hello(String), orfalse(Boolean) -
静态值的 列表,例如
[5, 6, 8](Int[]) 或["Hello", "Goodbye"](String[])。当使用受支持的数据库(PostgreSQL、CockroachDB 和 MongoDB)时,这些在 Prisma ORM 版本4.0.0及更高版本中可用¥Lists of static values, such as
[5, 6, 8](Int[]) or["Hello", "Goodbye"](String[]). These are available in Prisma ORM versions4.0.0and later, when using supported databases (PostgreSQL, CockroachDB and MongoDB) -
JSON 数据。请注意,JSON 需要在
@default属性内用双引号括起来,例如:@default("[]")。如果你想要提供 JSON 对象,则需要将其用双引号括起来,然后使用反斜杠转义任何内部双引号,例如:@default("{ \"hello\": \"world\" }")。¥JSON data. Note that JSON needs to be enclosed with double-quotes inside the
@defaultattribute, e.g.:@default("[]"). If you want to provide a JSON object, you need to enclose it with double-quotes and then escape any internal double quotes using a backslash, e.g.:@default("{ \"hello\": \"world\" }").
有关连接器功能支持的信息,请参阅 属性函数参考文档。
¥Refer to the attribute function reference documentation for information about connector support for functions.
定义一个独特的字段
¥Defining a unique field
你可以向模型添加唯一属性,以便能够唯一标识该模型的各个记录。可以使用 @unique 属性在单个字段上定义唯一属性,也可以使用 @@unique 属性在多个字段(也称为复合或复合唯一约束)上定义唯一属性。
¥You can add unique attributes to your models to be able to uniquely identify individual records of that model. Unique attributes can be defined on a single field using @unique attribute, or on multiple fields (also called composite or compound unique constraints) using the @@unique attribute.
在以下示例中,email 字段的值必须是唯一的:
¥In the following example, the value of the email field must be unique:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
name String?
}
在以下示例中,authorId 和 title 的组合必须是唯一的:
¥In the following example, a combination of authorId and title must be unique:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
categories Category[] @relation(references: [id])
@@unique([authorId, title])
}
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
categories Category[] @relation(references: [id])
@@unique([authorId, title])
}
关系数据库中的约束名称
你可以选择在基础数据库中定义 自定义唯一约束名称。
¥Constraint names in relational databases
You can optionally define a custom unique constraint name in the underlying database.
默认情况下,Prisma 客户端查询中该字段的名称将为 authorId_title。
¥By default, the name of this field in Prisma Client queries will be authorId_title.
你还可以使用 @@unique 属性的 name 字段为复合唯一约束提供你自己的名称:
¥You can also provide your own name for the composite unique constraint using the @@unique attribute's name field:
model Post {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
title String
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId String @db.ObjectId
categories Category[] @relation(references: [id])
@@unique(name: "authorTitle", [authorId, title])
}
authorId_title 字段现在将命名为 authorTitle。
¥The authorId_title field will now be named authorTitle instead.
请参阅 使用复合唯一标识符 上的文档,了解如何与 Prisma Client 中的复合唯一约束进行交互。
¥Refer to the documentation on working with composite unique identifiers to learn how to interact with a composite unique constraints in Prisma Client.
复合类型唯一约束
¥Composite type unique constraints
在 3.12.0 及更高版本中使用 MongoDB 提供程序时,你可以使用语法 @@unique([compositeType.field]) 对 复合型 的字段定义唯一约束。与其他字段一样,复合类型字段可以用作多列唯一约束的一部分。
¥When using the MongoDB provider in version 3.12.0 and later, you can define a unique constraint on a field of a composite type using the syntax @@unique([compositeType.field]). As with other fields, composite type fields can be used as part of a multi-column unique constraint.
以下示例基于 User 模型的 email 字段和 User.address 中使用的 Address 复合类型的 number 字段定义多列唯一约束:
¥The following example defines a multi-column unique constraint based on the email field of the User model and the number field of the Address composite type which is used in User.address:
type Address {
street String
number Int
}
model User {
id Int @id
email String
address Address
@@unique([email, address.number])
}
如果有多个嵌套复合类型,则可以链接此表示法:
¥This notation can be chained if there is more than one nested composite type:
type City {
name String
}
type Address {
number Int
city City
}
model User {
id Int @id
address Address[]
@@unique([address.city.name])
}
定义索引
¥Defining an index
你可以通过模型上的 @@index 在模型的一个或多个字段上定义索引。以下示例定义基于 title 和 content 字段的多列索引:
¥You can define indexes on one or multiple fields of your models via the @@index on a model. The following example defines a multi-column index based on the title and content field:
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
title String
content String?
@@index([title, content])
}
关系数据库中的索引名称
你可以选择在基础数据库中定义 自定义索引名称。
¥Index names in relational databases
You can optionally define a custom index name in the underlying database.
定义复合类型索引
¥Defining composite type indexes
在 3.12.0 及更高版本中使用 MongoDB 提供程序时,你可以使用语法 @@index([compositeType.field]) 在 复合型 的字段上定义索引。与其他字段一样,复合类型字段可以用作多列索引的一部分。
¥When using the MongoDB provider in version 3.12.0 and later, you can define an index on a field of a composite type using the syntax @@index([compositeType.field]). As with other fields, composite type fields can be used as part of a multi-column index.
以下示例定义了基于 User 模型的 email 字段和 Address 复合类型的 number 字段的多列索引:
¥The following example defines a multi-column index based on the email field of the User model and the number field of the Address composite type:
type Address {
street String
number Int
}
model User {
id Int @id
email String
address Address
@@index([email, address.number])
}
如果有多个嵌套复合类型,则可以链接此表示法:
¥This notation can be chained if there is more than one nested composite type:
type City {
name String
}
type Address {
number Int
city City
}
model User {
id Int @id
address Address[]
@@index([address.city.name])
}
定义枚举
¥Defining enums
你可以在数据模型 你的数据库连接器是否支持枚举 中定义枚举,无论是原生还是在 Prisma ORM 级别。
¥You can define enums in your data model if enums are supported for your database connector, either natively or at Prisma ORM level.
枚举在 Prisma 架构数据模型中被视为 scalar 类型。因此,它们作为 默认情况下 的返回值包含在 Prisma 客户端查询 中。
¥Enums are considered scalar types in the Prisma schema data model. They're therefore by default included as return values in Prisma Client queries.
枚举是通过 enum 块定义的。例如,User 有 Role:
¥Enums are defined via the enum block. For example, a User has a Role:
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
}
enum Role {
USER
ADMIN
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
email String @unique
name String?
role Role @default(USER)
}
enum Role {
USER
ADMIN
}
定义复合类型
¥Defining composite types
复合类型是在 3.10.0 版本中添加到 mongodb 预览版功能标志下的,并且从版本 3.12.0 开始正式发布。
¥Composite types were added in version 3.10.0 under the mongodb Preview feature flag and are in General Availability since version 3.12.0.
复合类型目前仅在 MongoDB 上可用。
¥Composite types are currently only available on MongoDB.
复合类型(在 MongoDB 中称为 嵌入文档)通过允许你定义新的对象类型,支持将记录嵌入到其他记录中。复合类型的结构和类型化方式与 models 类似。
¥Composite types (known as embedded documents in MongoDB) provide support for embedding records inside other records, by allowing you to define new object types. Composite types are structured and typed in a similar way to models.
要定义复合类型,请使用 type 块。例如,采用以下架构:
¥To define a composite type, use the type block. As an example, take the following schema:
model Product {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
name String
photos Photo[]
}
type Photo {
height Int
width Int
url String
}
在本例中,Product 模型在 photos 中存储了 Photo 复合类型的列表。
¥In this case, the Product model has a list of Photo composite types stored in photos.
使用复合类型时的注意事项
¥Considerations when using composite types
复合类型仅支持有限的 attributes 集。支持以下属性:
¥Composite types only support a limited set of attributes. The following attributes are supported:
-
@default -
@map -
原生类型,例如
@db.ObjectId¥Native types, such as
@db.ObjectId
复合类型内部不支持以下属性:
¥The following attributes are not supported inside composite types:
-
@unique -
@id -
@relation -
@ignore -
@updatedAt
但是,仍然可以通过在使用复合类型的模型级别上使用 @@unique 属性来定义唯一约束。详细信息请参见 复合类型唯一约束。
¥However, unique constraints can still be defined by using the @@unique attribute on the level of the model that uses the composite type. For more details, see Composite type unique constraints.
可以通过在使用复合类型的模型级别上使用 @@index 属性来定义索引。详细信息请参见 复合型指标。
¥Indexes can be defined by using the @@index attribute on the level of the model that uses the composite type. For more details, see Composite type indexes.
使用函数
¥Using functions
Prisma 架构支持多个 functions 。 这些可用于在模型的字段上指定 默认值。
¥The Prisma schema supports a number of functions . These can be used to specify default values on fields of a model.
例如, createdAt 的默认值为 now() :
¥For example, the default value of createdAt is now() :
- Relational databases
- MongoDB
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
}
model Post {
id String @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
}
cuid() 和 uuid() 由 Prisma ORM 实现,因此在底层数据库模式中不是 "visible"。当使用 introspection by 手动更改 Prisma 架构 和 生成 Prisma 客户端 时,你仍然可以使用它们,在这种情况下,这些值将由 Prisma 客户端的 查询引擎 生成
¥cuid() and uuid() are implemented by Prisma ORM and therefore are not "visible" in the underlying database schema. You can still use them when using introspection by manually changing your Prisma schema and generating Prisma Client, in that case the values will be generated by Prisma Client's query engine
不同数据库对 autoincrement()、now() 和 dbgenerated(...) 的支持不同。
¥Support for autoincrement(), now(), and dbgenerated(...) differ between databases.
关系数据库连接器在数据库级别实现 autoincrement()、dbgenerated(...) 和 now()。MongoDB 连接器不支持 autoincrement() 或 dbgenerated(...),now() 在 Prisma ORM 级别实现。auto() 函数用于生成 ObjectId。
¥Relational database connectors implement autoincrement(), dbgenerated(...), and now() at database level. The MongoDB connector does not support autoincrement() or dbgenerated(...), and now() is implemented at the Prisma ORM level. The auto() function is used to generate an ObjectId.
关系
¥Relations
有关模型之间关系的更多示例和信息,请参阅 关系文档。
¥Refer to the relations documentation for more examples and information about relationships between models.
Prisma 客户端中的模型
¥Models in Prisma Client
查询(增删改查)
¥Queries (CRUD)
数据模型定义中的每个模型都会在生成的 Prisma 客户端 API 中产生大量 CRUD 查询:
¥Every model in the data model definition will result in a number of CRUD queries in the generated Prisma Client API:
这些操作可通过 Prisma 客户端实例上生成的属性进行访问。默认情况下,属性名称是模型名称的小写形式,例如 user 代表 User 型号,post 代表 Post 型号。
¥The operations are accessible via a generated property on the Prisma Client instance. By default the name of the property is the lowercase form of the model name, e.g. user for a User model or post for a Post model.
以下示例说明了如何使用 Prisma 客户端 API 中的 user 属性:
¥Here is an example illustrating the use of a user property from the Prisma Client API:
const newUser = await prisma.user.create({
data: {
name: 'Alice',
},
})
const allUsers = await prisma.user.findMany()
类型定义
¥Type definitions
Prisma Client 还生成反映模型结构的类型定义。这些是生成的 @prisma/client 节点模块的一部分。
¥Prisma Client also generates type definitions that reflect your model structures. These are part of the generated @prisma/client node module.
使用 TypeScript 时,这些类型定义可确保所有数据库查询完全类型安全并在编译时进行验证(甚至使用 select 或 include 的部分查询)。
¥When using TypeScript, these type definitions ensure that all your database queries are entirely type safe and validated at compile-time (even partial queries using select or include ).
即使使用纯 JavaScript,类型定义仍然包含在 @prisma/client 节点模块中,从而在编辑器中启用 IntelliSense/自动补齐等功能。
¥Even when using plain JavaScript, the type definitions are still included in the @prisma/client node module, enabling features like IntelliSense/autocompletion in your editor.
注意:实际类型存储在
.prisma/client文件夹中。@prisma/client/index.d.ts导出该文件夹的内容。¥Note: The actual types are stored in the
.prisma/clientfolder.@prisma/client/index.d.tsexports the contents of this folder.
例如,上面的 User 模型的类型定义如下所示:
¥For example, the type definition for the User model from above would look as follows:
export type User = {
id: number
email: string
name: string | null
role: string
}
请注意,默认情况下,关系字段 posts 和 profile 不包含在类型定义中。但是,如果你需要 User 类型的变体,你仍然可以使用某些 Prisma Client 生成的辅助程序类型 来定义它们(在这种情况下,这些辅助类型将称为 UserGetIncludePayload 和 UserGetSelectPayload)。
¥Note that the relation fields posts and profile are not included in the type definition by default. However, if you need variations of the User type you can still define them using some of Prisma Client's generated helper types (in this case, these helper types would be called UserGetIncludePayload and UserGetSelectPayload).
局限性
¥Limitations
记录必须是唯一可识别的
¥Records must be uniquely identifiable
Prisma ORM 目前仅支持至少具有一个唯一字段或字段组合的模型。实际上,这意味着每个 Prisma 模型必须至少具有以下属性之一:
¥Prisma ORM currently only supports models that have at least one unique field or combination of fields. In practice, this means that every Prisma model must have either at least one of the following attributes:
-
@id或@@id用于单字段或多字段主键约束(每个模型最多一个)¥
@idor@@idfor a single- or multi-field primary key constraint (max one per model) -
@unique或@@unique用于单字段或多字段唯一约束¥
@uniqueor@@uniquefor a single- or multi-field unique constraint