TypeScript 项目中的 PlanetScale 自检
使用 Prisma ORM 检查你的数据库
¥Introspect your database with Prisma ORM
出于本指南的目的,我们将使用包含三个表的演示 SQL 架构:
¥For the purpose of this guide, we'll use a demo SQL schema with three tables:
CREATE TABLE `Post` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`createdAt` datetime(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3),
`updatedAt` datetime(3) NOT NULL,
`title` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`content` varchar(191) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`published` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`authorId` int NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `Post_authorId_idx` (`authorId`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE `Profile` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`bio` varchar(191) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`userId` int NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `Profile_userId_key` (`userId`),
KEY `Profile_userId_idx` (`userId`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE TABLE `User` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`email` varchar(191) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(191) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `User_email_key` (`email`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
Expand for a graphical overview of the tables
邮政
¥Post
| 栏目名称 | 类型 | 首要的关键 | 外键 | 必需的 | 默认 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | int | **✔️ ** | 不 | **✔️ ** | 自动递增 |
createdAt | datetime(3) | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | now() |
updatedAt | datetime(3) | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | |
title | varchar(255) | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | * |
content | varchar(191) | 不 | 不 | 不 | * |
published | tinyint(1) | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | false |
authorId | int | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | * |
轮廓
¥Profile
| 栏目名称 | 类型 | 首要的关键 | 外键 | 必需的 | 默认 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | int | **✔️ ** | 不 | **✔️ ** | 自动递增 |
bio | varchar(191) | 不 | 不 | 不 | * |
userId | int | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | * |
用户
¥User
| 栏目名称 | 类型 | 首要的关键 | 外键 | 必需的 | 默认 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id | int | **✔️ ** | 不 | **✔️ ** | 自动递增 |
name | varchar(191) | 不 | 不 | 不 | * |
email | varchar(191) | 不 | 不 | **✔️ ** | * |
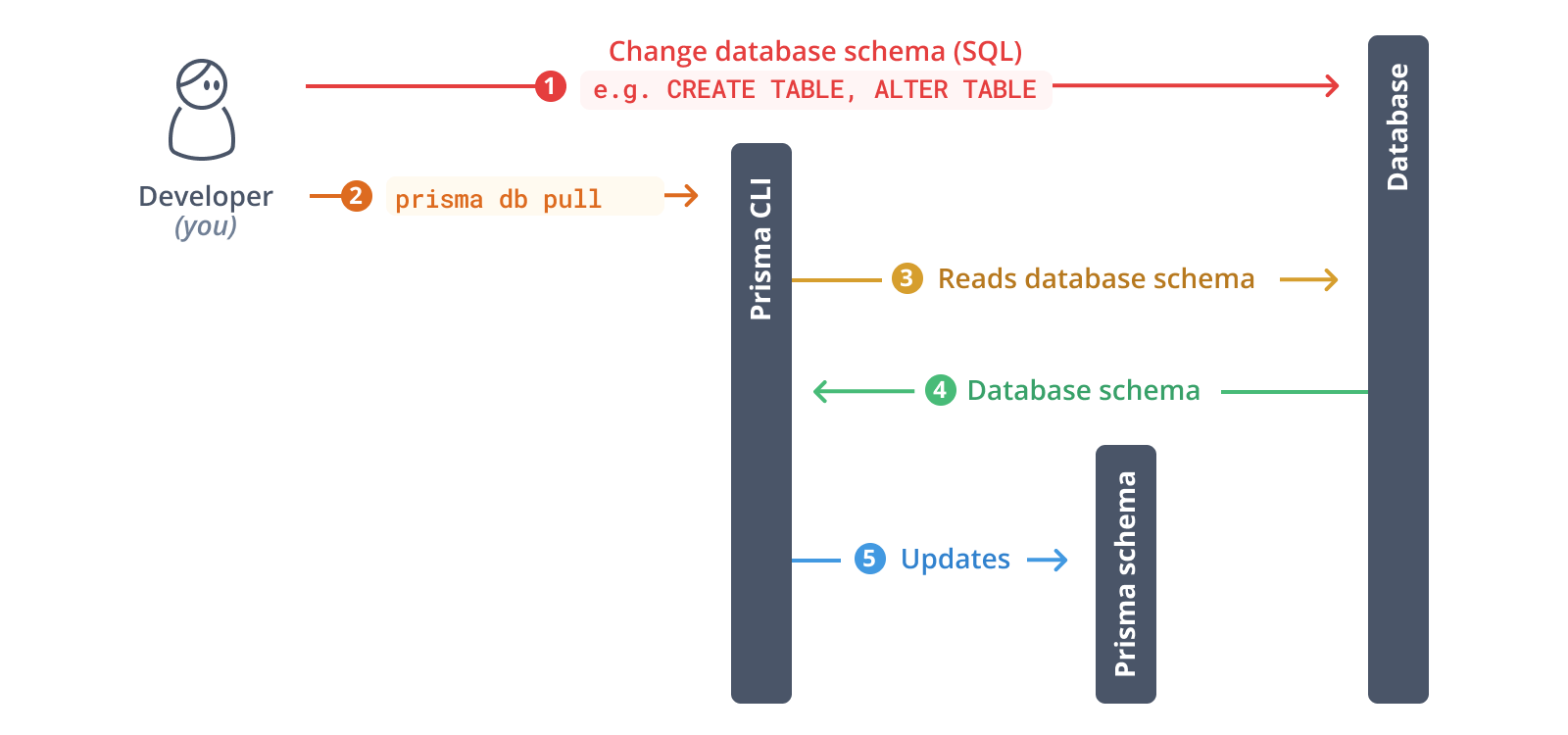
下一步,你将检查你的数据库。内省的结果将是 Prisma 架构内的 数据模型。
¥As a next step, you will introspect your database. The result of the introspection will be a data model inside your Prisma schema.
运行以下命令来检查你的数据库:
¥Run the following command to introspect your database:
npx prisma db pull
此命令读取在 .env 中定义的 DATABASE_URL 环境变量并连接到你的数据库。一旦建立连接,它就会内省数据库(即读取数据库模式)。然后,它将数据库架构从 SQL 转换为 Prisma 数据模型。
¥This command reads the DATABASE_URL environment variable that's defined in .env and connects to your database. Once the connection is established, it introspects the database (i.e. it reads the database schema). It then translates the database schema from SQL into a Prisma data model.
自省完成后,你的 Prisma 架构将更新:
¥After the introspection is complete, your Prisma schema is updated:
数据模型现在看起来类似于:
¥The data model now looks similar to this:
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime
title String @db.VarChar(255)
content String?
published Boolean @default(false)
authorId Int
@@index([authorId])
}
model Profile {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
bio String?
userId Int @unique
@@index([userId])
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
}
有关架构定义的详细信息,请参阅 Prisma 架构参考。
¥Refer to the Prisma schema reference for detailed information about the schema definition.
Prisma 的数据模型是数据库模式的声明性表示,并作为生成的 Prisma 客户端库的基础。你的 Prisma 客户端实例将公开针对这些模型定制的查询。
¥Prisma's data model is a declarative representation of your database schema and serves as the foundation for the generated Prisma Client library. Your Prisma Client instance will expose queries that are tailored to these models.
然后,你需要使用 关系字段 添加数据之间任何缺失的关系:
¥You will then need to add in any missing relations between your data using relation fields:
model Post {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
createdAt DateTime @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime
title String @db.VarChar(255)
content String?
published Boolean @default(false)
author User @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int
@@index([authorId])
}
model Profile {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
bio String?
user User @relation(fields: [userId], references: [id])
userId Int @unique
@@index([userId])
}
model User {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
email String @unique
name String?
posts Post[]
profile Profile?
}
之后,第二次对数据库运行内省:
¥After this, run introspection on your database for a second time:
npx prisma db pull
Prisma Migrate 现在将保留手动添加的关系字段。
¥Prisma Migrate will now keep the manually added relation fields.
由于关系字段是虚拟的(即它们不直接在数据库中体现),因此你可以在 Prisma 模式中手动重命名它们,而无需接触数据库。
¥Because relation fields are virtual (i.e. they do not directly manifest in the database), you can manually rename them in your Prisma schema without touching the database.
在此示例中,数据库架构遵循 Prisma ORM 模型的 命名约定。这优化了生成的 Prisma 客户端 API 的人机工程学。
¥In this example, the database schema follows the naming conventions for Prisma ORM models. This optimizes the ergonomics of the generated Prisma Client API.
Using custom model and field names
但有时,你可能希望对 Prisma 客户端 API 中公开的列和表的名称进行其他更改。一个常见的例子是将数据库模式中经常使用的 Snake_case 表示法转换为 PascalCase 和 CamelCase 表示法,这对于 JavaScript/TypeScript 开发者来说感觉更自然。
¥Sometimes though, you may want to make additional changes to the names of the columns and tables that are exposed in the Prisma Client API. A common example is to translate snake_case notation which is often used in database schemas into PascalCase and camelCase notations which feel more natural for JavaScript/TypeScript developers.
假设你从基于 Snake_case 表示法的内省中获得了以下模型:
¥Assume you obtained the following model from introspection that's based on snake_case notation:
model my_user {
user_id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
first_name String?
last_name String @unique
}
如果你为此模型生成了 Prisma 客户端 API,它会在其 API 中选取 Snake_case 表示法:
¥If you generated a Prisma Client API for this model, it would pick up the snake_case notation in its API:
const user = await prisma.my_user.create({
data: {
first_name: 'Alice',
last_name: 'Smith',
},
})
如果你不想在 Prisma 客户端 API 中使用数据库中的表和列名称,你可以使用 @map 和 @@map 配置它们:
¥If you don't want to use the table and column names from your database in your Prisma Client API, you can configure them with @map and @@map:
model MyUser {
userId Int @id @default(autoincrement()) @map("user_id")
firstName String? @map("first_name")
lastName String @unique @map("last_name")
@@map("my_user")
}
通过这种方法,你可以根据自己的喜好命名模型及其字段,并使用 @map(对于字段名称)和 @@map(对于模型名称)来指向基础表和列。你的 Prisma 客户端 API 现在如下所示:
¥With this approach, you can name your model and its fields whatever you like and use the @map (for field names) and @@map (for models names) to point to the underlying tables and columns. Your Prisma Client API now looks as follows:
const user = await prisma.myUser.create({
data: {
firstName: 'Alice',
lastName: 'Smith',
},
})
在 配置你的 Prisma 客户端 API 页面上了解更多相关信息。
¥Learn more about this on the Configuring your Prisma Client API page.